The first things we know from this course were abstract data types and object-oriented programming. And they did sound "abstract" to me. During the days that working on assignment1, my group went through a very difficult time. So did things in lab. I was told that I didn't understand OOP at all..., which hurt me a lot. However, after finishing assignment1 and the third-week(or forth-) lab, I felt things were clearer. Finally, our work got a very high and very surprising mark. Then I started to worry about test 1, because I didn't think I can handle it and I even wanted to give up (mainly because of suffer from doing assignment, haha). However, the result surprised me again.
Then we started to learn about recursion, which was much more difficult than class and subclass. At first, I thought it was quite easy, because the only thing we need to do is trace recursion, which was easiest part for recursion. That was the first time I felt lab was easy... Thanks to professor, knowing how to trace recursions made a easy start. After that, labs became quite difficult. And after learning trees, I realized that the purpose of the recursion related exercise was to introduce us to the mechanics of recursive thinking, which help us writing more complicated codes such as codes about trees and so on. it was the the time of learning recursion that I read a lot of contents from some classic books of python.
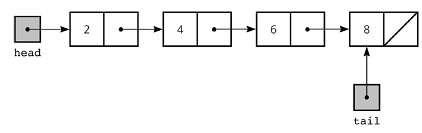
After recursion, we started to learn trees. I have to say that there was nothing called "easy" for CSC148. Tree is amazing, which also bring lots of "amazing" difficulties for me. I love the way that trees work, it was brilliant. The one who invented it was extremely intelligent. My favorite tree was BST, it is a good way to collect and filter information. Then we took tests 2. It was a disaster for me, because I forgot to go through Linked List... So I did quite bad because of losing all the marks of the last question. This gave me lesson that I'm supposed to review every day and every week and make sure I understand everything w learnt clearly.
The last week, we learnt running time analyst that was quite similar with we we learnt in CSC165. It was just like a review session and there was nothing very difficult.
Overall, I enjoy CSC148 a lot, although I cannot deny it was not easy for me. However, I love challenges and also I love the things I learn from those challenges. I think I'm at the gate of computer SCIENCE now. I'll keep reading, writing, thinking and practicing as I did in this semester.
I appreciate my professor bringing those amingzing courses to us. I appreciate my TA who was very patient! Thank you for reading my SLOG!
I love CS!